MODELIMEX Online Shop 1/72 Fokker S.IV (Holland) your favourite model shop
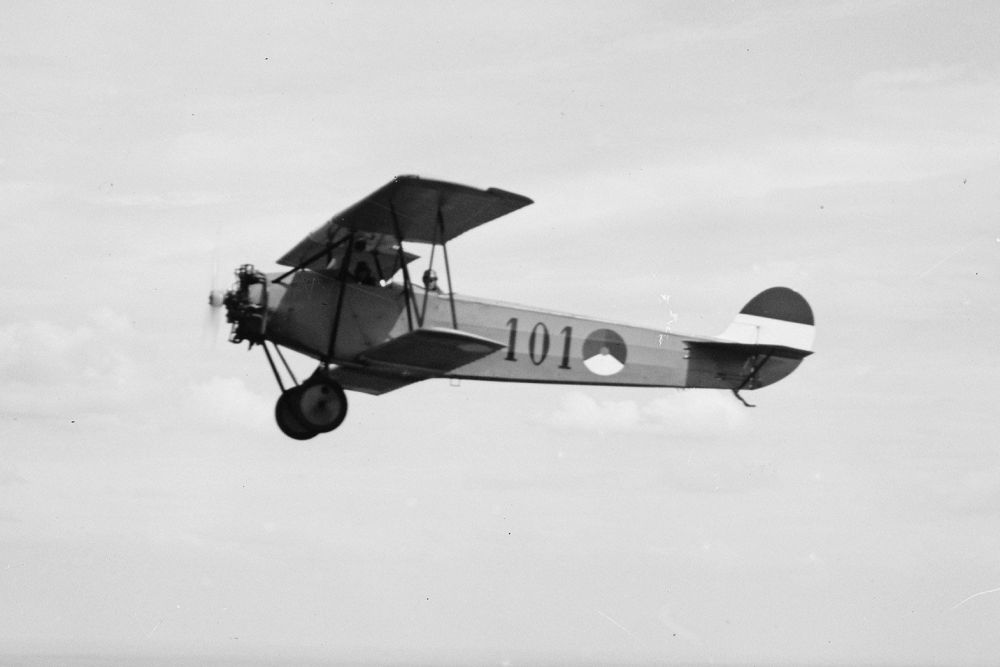
The Fokker S.IV was a military trainer aircraft produced in the Netherlands in the mid-1920s. It was a conventional, single-bay biplane with staggered wings of unequal span braced with N-struts, essentially a radial-engined development of the S.III.

Fokker S.IV (S4) TracesOfWar.nl
The Fokker D.V (Fokker designation M.22) was a German biplane fighter of World War I . Design and development After the disappointing performance of his D.I through D.IV, Fokker resolved to produce a smaller, lighter rotary-powered design.

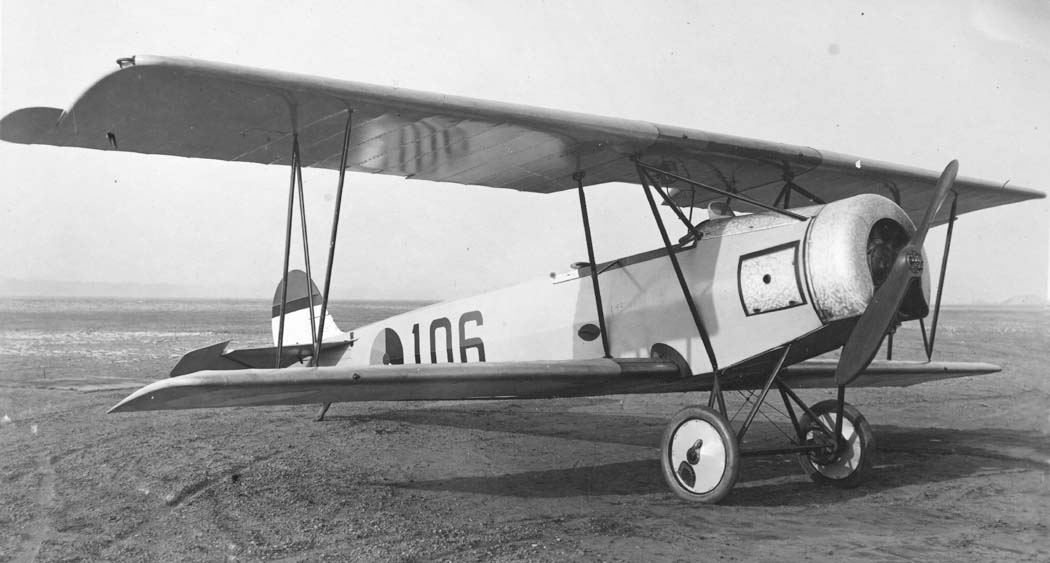
Aircraft Photo of 119 Fokker S.IV Netherlands Air Force 404081
The Fokker S.IV was a military trainer aircraft produced in the Netherlands in the mid-1920s. It was a conventional, single-bay biplane with staggered wings of unequal span braced with N-struts, essentially a radial engined development of the S.III. Specifications (S.IV) Crew 2 Length 8.55 m (28 ft 1 in)

Fokker S.IV
Fokker, legally N.V. Koninklijke Nederlandse Vliegtuigenfabriek Fokker ( lit. 'Royal Dutch Aircraft Factory Fokker'), was a Dutch aircraft manufacturer named after its founder, Anthony Fokker. The company operated under several different names. It was founded in 1912 in Berlin, Germany, and became famous for its fighter aircraft in World War I.

Fokker S.IV
The most common alternative to neonicotinoids (89% of cases) was the use of another chemical insecticide (mostly pyrethroids). However, in 78% of cases, at least one non-chemical alternative method could replace neonicotinoids (e.g. microorganisms, semiochemicals or surface coating). The relevance of non-chemical alternatives to neonicotinoids.

NVM 50.10.013 Fokker SIV, lesvliegtuig Modelbouwtekeningen.nl
The Fokker D.IV was a German fighter biplane of World War I, a development of the D.I.

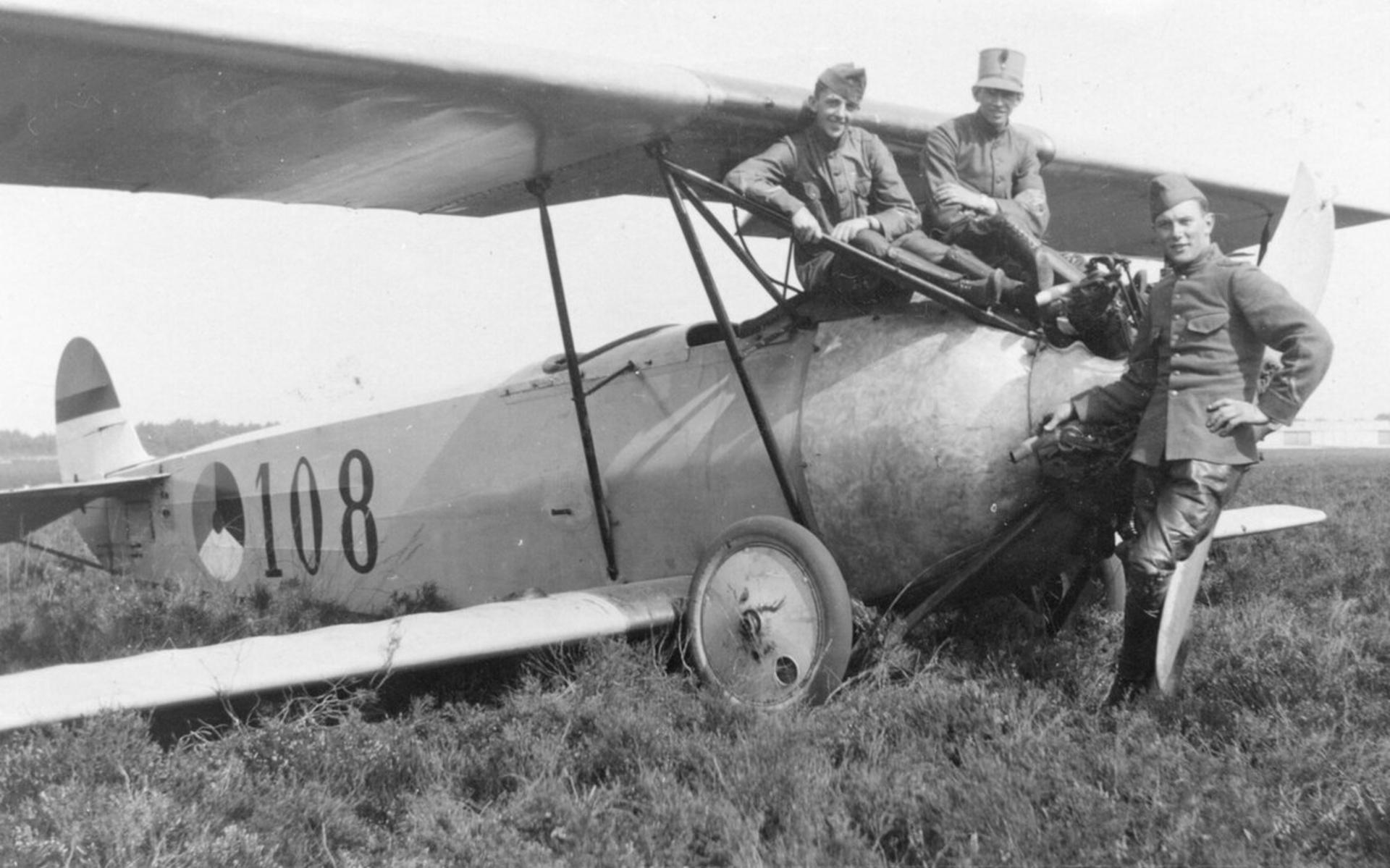
Fokker SIV, PHSIV / 108, Aviodrome Museum ABPic
Given the Fokker designation of M.15, the E.IV was essentially a lengthened Fokker E.III powered by the 119 kW (160 hp) Oberursel U.III two-row, 14-cylinder rotary engine, a copy of the Gnome Double Lambda. The more powerful engine was intended to enable the Eindecker to carry two or three 7.92 mm (.312 in) machine guns, thereby increasing its.

Fokker S.IV LVA 108 Aviodrome
The Fokker S.IV was a military trainer aircraft produced in the Netherlands in the mid-1920s. It was a conventional, single-bay biplane with staggered wings of unequal span braced with N-struts, essentially a radial-engined development of the S.III.The pilot and instructor sat in tandem, open cockpits and the undercarriage was of fixed, tailskid type with a cross-axle between the main units.
Fokker S.IV
Nouvelle-Aquitaine. Nouvelle-Aquitaine (Occitan: Nòva Aquitania, Basque: Akitania Berria, Poitevin-Saintongeais: Novéle-Aguiéne; all mean New Aquitaine in English) is the largest region of France. It stretches from the Spanish border and Pyrenees in the south, to the Loire Valley 500 km to the north, and from the Atlantic coastal sands in.

Fokker S.IV
Nouvelle-Aquitaine, the largest of France's 13 metropolitan regions, which was created in 2016 by the union of Aquitaine, Poitou-Charentes, and Limousin. It is bounded by the regions of Pays de la Loire, Centre, Auvergne-Rhone-Alpes, and Occitanie and by Spain and the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Bordeaux.

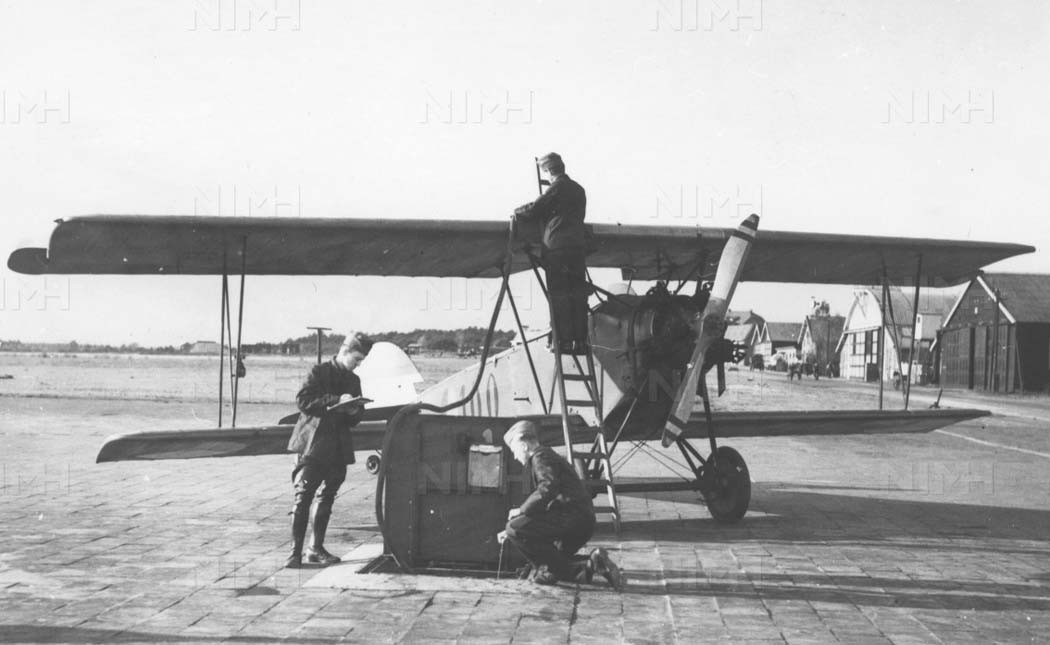
Enige overgebleven Fokkerlesvliegtuig uit 1924 gerestaureerd in Aviodrome Flevopost
First flown in 1924, the S.IV was the standard elementary trainer in the Dutch army air force. This aircraft has been refitted with a 130-hp Armstrong-Siddeley Mongoose engine. It is seen with another S.IV, 116, and two Fokker C.1 advanced trainers, 500 and 539. Photo from: Bodo Sandberg collection

Fokker S.IV
The Fokker S.IV has been the most used training aircraft at the Soesterbergse Vliegschool (flight school) of the LVA. From 1924 to 1940 it was the standard trainer of the Air Force. A total of 31 S.IVs were built, which flew with the LVA in the Indies in addition to the LVA.
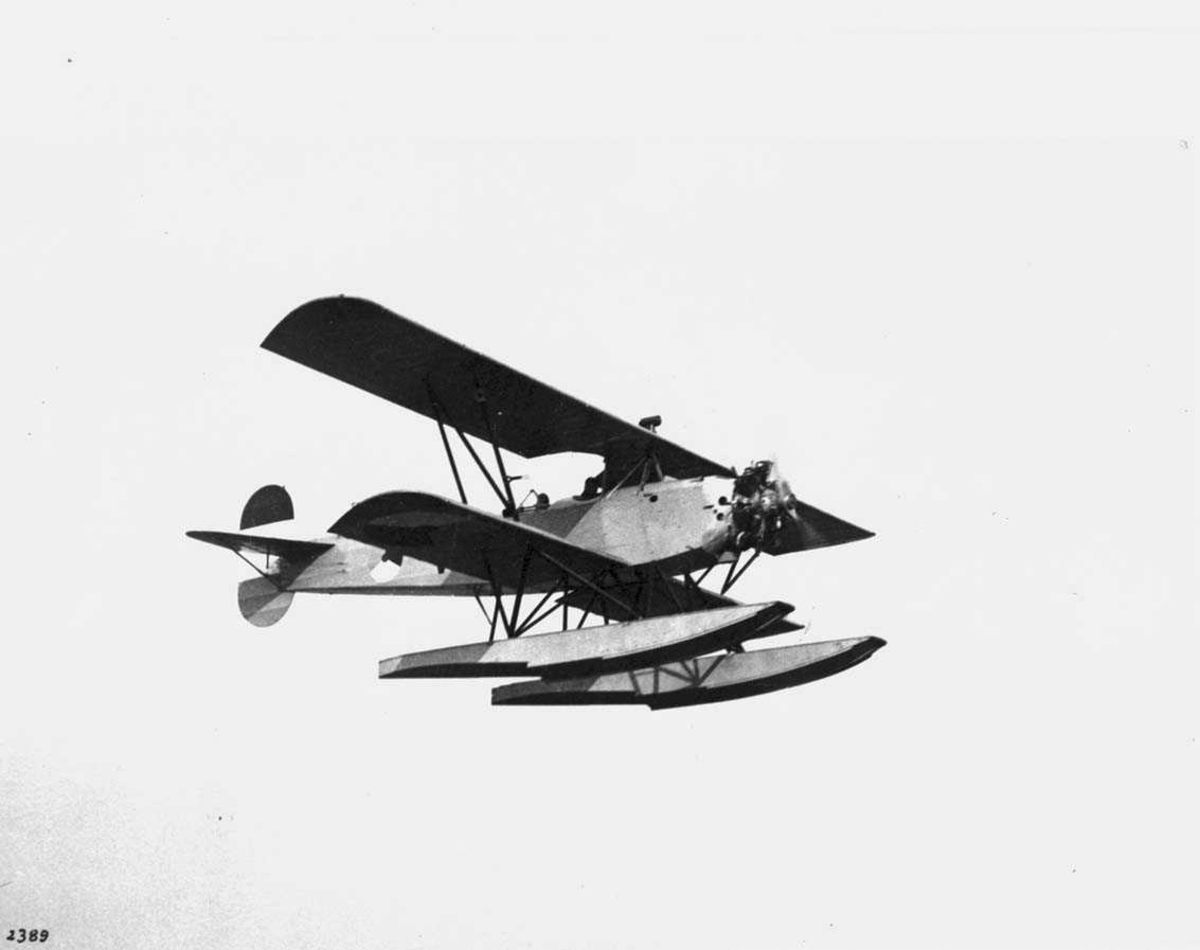

Luftfoto. Ett fly i lufta, Fokker S.IV Norsk Luftfartsmuseum / DigitaltMuseum
The Fokker F.IV was an airliner designed in the Netherlands in the early 1920s, with only two ever made, both for the United States Army Air Service (designated T-2 ). The aircraft made the first non-stop coast to coast flight of the continental United States in May 1923.
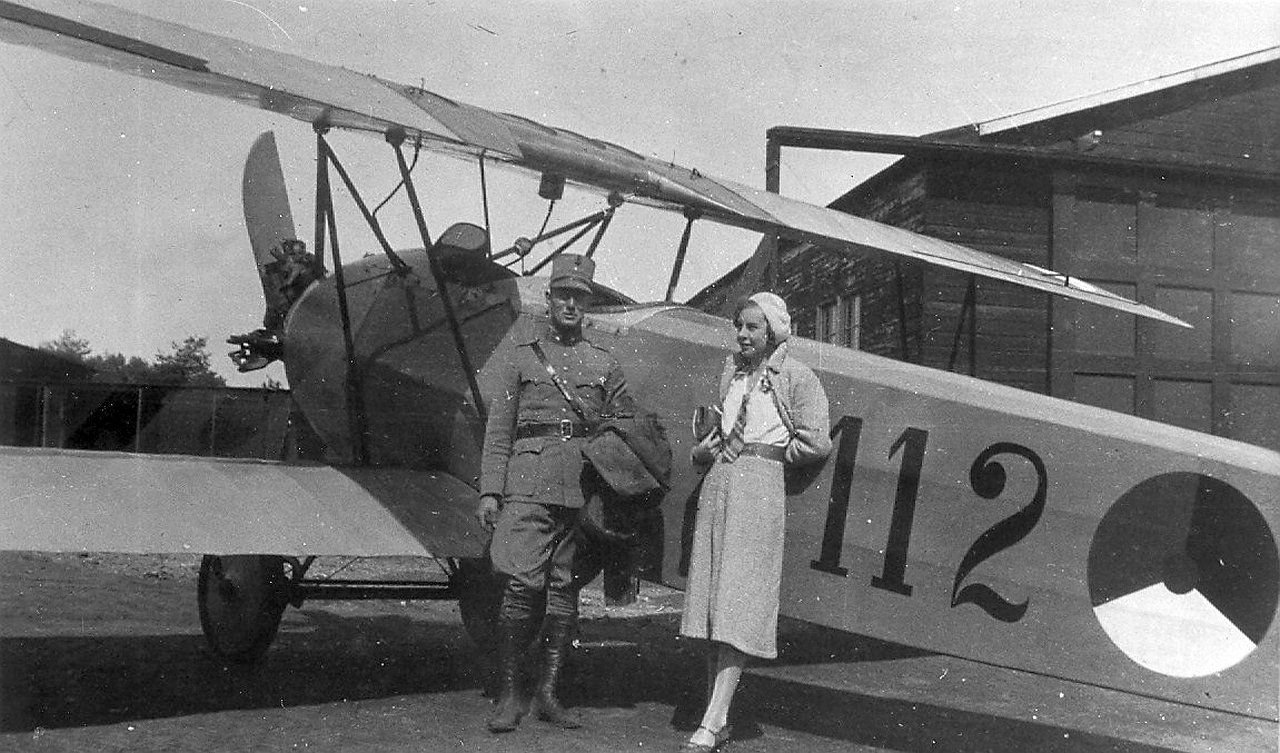

Fokker S.IV
The Fokker S.IV was a military trainer aircraft produced in the Netherlands in the mid-1920s. It was a conventional, single-bay biplane with staggered wings of unequal span braced with N-struts, essentially a radial-engined development of the S.III. The pilot and instructor sat in tandem, open.
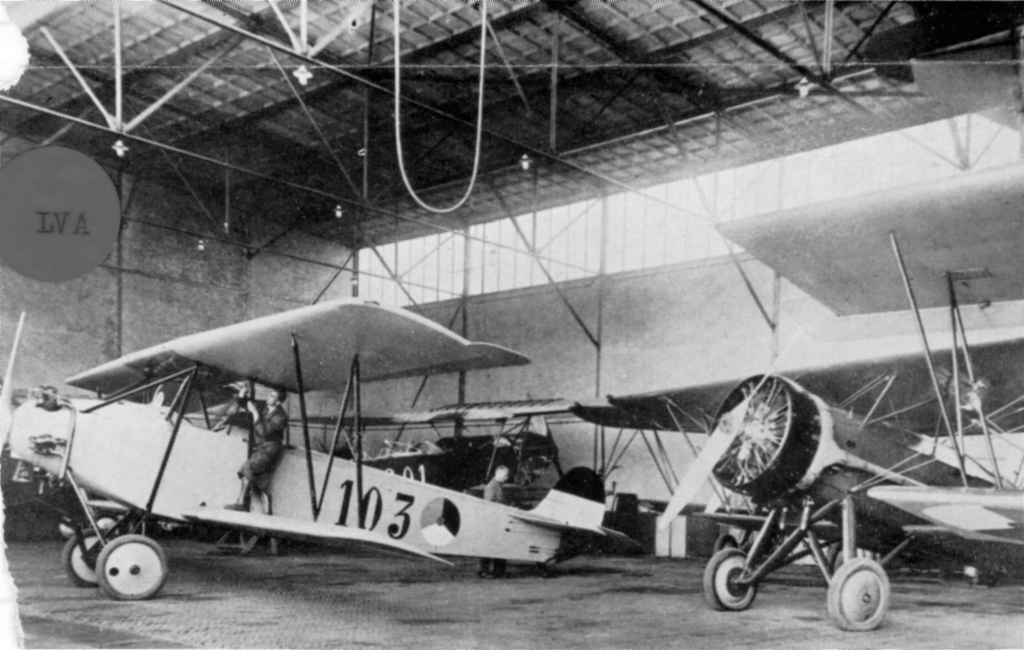

Fokker S.IV (English)
Fokker's Mercedes-powered D.I and D.IV biplane fighters were also outperformed by their contemporaries, and suffered from so many structural and quality-control problems that they were relegated to training duties. Technology had moved on, and Fokker had been left behind.
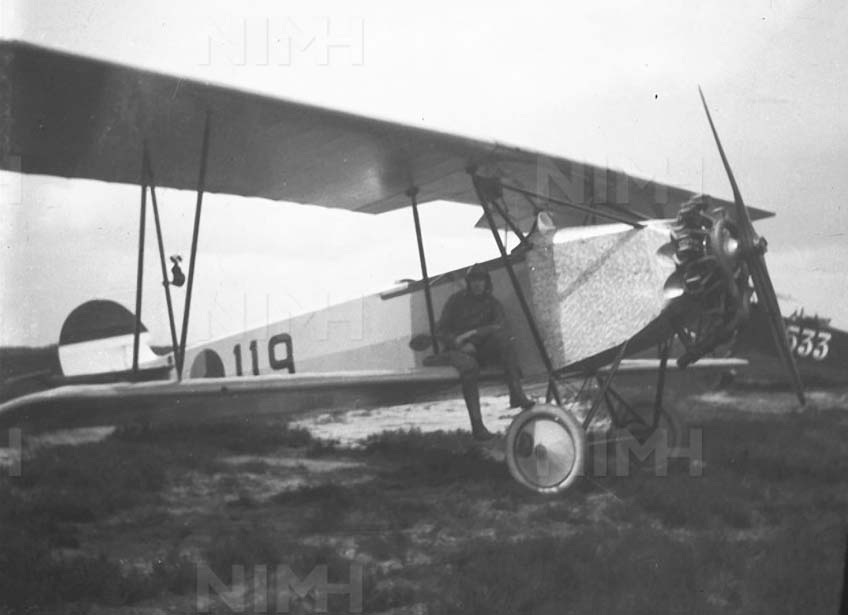

Fokker S.IV
The Fokker D.IV was a German fighter biplane of World War I, a development of the D.I. [2] [3] Development The Fokker D.IV had a more powerful Mercedes D.III engine, and was the first Fokker front-line design to use ailerons in place of wing warping from the start for roll control. [4] Operational history